
This changing scenario of the healthcare industry has drastically changed the IT requirements of hospitals. There are clear challenges within the current healthcare ecosystem that must be overcome before the healthcare revolution is realised.
1. Over the last few years, the Indian healthcare sector has been rapidly evolving. How has this affected the software/IT needs of hospitals?
Healthcare is undergoing a distinct movement along a logical trajectory from its historical focus on acute care i.e. dealing with immediate and severe outbreaks of illness, to chronic care, continuous care for long term illness that may reduce acute cases to preventive care, i.e. care focussed on early detection and treatment of illness, including immunisation, ultimately leading to predictive care, i.e. not waiting for early signs of illness but predicting and thwarting it before the illness has the chance to take root. This revolution would move us away from a curative drug based healthcare towards consulting/service based healthcare with focus on lifestyle, and adapting behaviour to prevent and cut out the roots of any instance of illness.
This changing scenario of the healthcare industry has drastically changed the IT requirements of hospitals. There are clear challenges within the current healthcare ecosystem that must be overcome before the healthcare revolution is realised.
The challenges are:
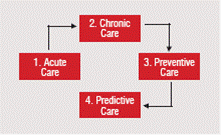
2. How have the suppliers handled this?
Business models are currently focussed on Acute Care across healthcare ecosystem. Models catering to Chronic, and more advanced Preventive care need to be explored by insurance companies and healthcare service providers alike.The hospitals and the suppliers will now have to start looking at the following:
3. How have Indian hospitals fared in terms of healthcare IT adoptation as compared to other countries in Asia/Rest of the world?
The structure within which healthcare is carried out varies from country to country—and sometimes even within national boundaries.
The most fundamental property affecting the Indian healthcare sector is the multi-faceted demographic and socio-economic profile of the country.
The emergence of corporate hospitals on a larger scale is another important development. The corporate entry into healthcare is important for the professionalism of hospital management. Till recently, modern management systems had not penetrated most healthcare institutions, with some notable exceptions. Most hospitals would organise their resources and manpower within structures that had evolved rather than been designed. The processes would be structured to ensure multiple points of control rather than patient convenience. Information capture would be rudimentary and information rarely integrated beyond that required for reporting purposes, because of which any data-based quality control would not be possible.
With corporate entities entering the healthcare sector, they are introducing managerial practices and tools, which they had been using for long, in the hospitals that they are promoting. To understand the Indian hospital landscape, given below is the classification of various types of hospitals:
Primary hospitals
These are the hospitals that are in the village or the local locality level. The concept of these hospitals is “Everything for Everybody”
Secondary hospitals
These are the hospitals that run on the concept “Everything for Everybody, but at a Higher Level”.
Tertiary care hospitals
These are the hospitals that give “Expert Care for Everything”. These can be corporate or Government. On the government side these are the hospitals with the Medical Colleges.
Super speciality hospital (One speciality)
These are the hospitals where only one type of vertical or speciality is handled.
An important and positive development taking place in the Indian healthcare sector is the use of information technology for purposes such as computerization of medical records, networking of various departments in a hospital, and providing of tele-medicine services.
With advent of Information Technology in Indian healthcare, disintermediation has occurred in such a way that the primary & secondary level hospitals can have a direct access to the Super Speciality Hospitals, in a collaborative way. The new organisation model not only removes the intermediate layers but also provides a conducive atmosphere for primary level hospitals, to work symbiotically with the Super Speciality hospitals. This will be a win-win situation for both partners.
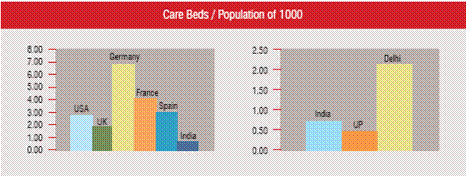
This graph depicts the ratio of number of beds to number of patients of a few developed countries against that of India. As of now India is very low on this ratio, with just 0.75 bed per 1000 population, as compared to the other countries.
4. What developments are likely to occur in the healthcare IT landscape in India in the near future, how are you preparing for it?
The following developments will have to necessarily take place in healthcare:
Srishti's integrated Healthcare solutions provide the ability to support modern healthcare services, additionally future-proofing initiatives, delivery models and emerging trends that would soon dominate this sector. Built on the philosophies of integration of the entire spectrum of healthcare technology enablers plus Srishti's powerful tool-kit approach (that makes healthcare services avoid constraints from technology limitations), PARAS is the answer to the need for a one-stop technology for healthcare.
Srishti software offers a complete healthcare information management system (HIMS) which involves implementation of clinical system for managing EPR and development of clinical care pathways. This clinical system can be integrated seamlessly with the hospital administration system Integrated electronic patient record system (EPR) - This gives the complete demographic information of the patient i.e. age, name, sex, etc., patient’s present illness information which includes details on present illness, history, medication, consultant notes, etc.
PARAS toolkit facilitates remote diagnosis or tele-medicine. This separates point of care and diagnostic resources, hence enabling healthcare providers to extend their reach to geographies where such resources are not available to patients.
5. How has IT changed the patient care landscape in India? With the help of IT, patient care has improved drastically. In IT enabled hospitals, the bed turnaround ratio has increased by as much as 10%, which is a big advantage. Hence, the investment towards enabling IT gets recovered in a few months. Enumerated below are the advantages of enabling IT in hospitals:
Thus IT helps in maximising returns on every penny spent.
6. As a software company what are your views on the potential of the healthcare IT sector in India? Healthcare is an emerging industry where the scope is unlimited. We have a vision and that’s what we aim to sell. Our differentiator lies in the fact that we don’t just sell functionality, but functionality with a vision.