
Introduction
Maximising the life span of a human being is the ultimate goal of every development in the medical field. The technical advancements’ contribution is tremendous towards the healthcare industry. In this regard, the communication technology helps in speeding up of the process. When the speed has been concentrated, the process should not become expensive. The developments in the medical field must be cost effective and painless. In this vision, the recent developments in Information and Communication Technology (ICT) such as communication through e-mail, video conferencing and mobile applications pave a path for the effective treatment and prevention of disease in a short span of time with less money.
Choice of Internet
In earlier days fixing an appointment with a physician itself was a painful job, but today the trend has been changed because of the cloud enabled database systems. [1] Physician prefer to have a website through which the patients can fix their appointment according to their convenience. On the other hand it is convenient for the doctors to store the patient’s details in the web. Since the diagnosis, prescription, treatment and follow up details are perfectly recorded in the database it is easy for them to analyse their patient’s condition at any time through the internet.
In case of decision making the physicians have a choice of searching for the similar case histories not in a huge volume of manual records but in a mouse click. They can find the related case histories either from the internet or from their own patients’ particulars kept in the cloud. Since, the prescription and follow up details are documented in the cloud, decision about the treatment can be taken instantly.
The medical reports in terms of clinical data and medical images could have been sent to the physicians for their decision about the treatment instantly through their e-mail ids which helps to avoid delay in the treatment. Recent trend in most of the scan centres are, sending their reports to the physicians directly through e-mail before the patient reaches the clinic which makes the procedure much simpler and faster.
Video Conferencing
In the process of diagnosis [2] when there is a necessity for an opinion from a specialist who is geographically separated, the consultation could be done through video conferencing. The patient and the doctors can meet through the virtual platform where the specialist can examine the patient and analyse his/her clinical reports and medical images. The doctors at both ends can discuss and make decisions about the diagnosis and treatment at the same time. Video conferencing avoids the overhead of travel unless a specialised treatment is required.
Mobile Apps
At times patients prefer to validate their clinical reports with the reliable resources. In that case they have the option of confirming their report through certain mobile apps. Worldwide, mobile phones have become ubiquitous and they have wide coverage at an unprecedented rate in almost every field. Healthcare is not an exception. Thousands of healthcare apps have been put out on the two prominent platforms Android and iOS, for free of cost. There are around 150,000 mobile apps available for healthcare [3]. In 2014 these apps usage were not less than 100,000.
Mobile apps support all kinds of patients, Diabetic and blood pressure patients can rely on Blood Pressure monitoring apps such as Instant Blood Pressure, Blood Pressure Check, Finger Blood Pressure and Diabetic control apps [4] such as Glooko, Glucosio, MySugr and BG monitor for their clinical data analysis. Similarly the Paediatric liver study app, an imaging app, is used to predict certain rare Paediatric liver disease, in the same manner Autism track, iprompts and the social express apps have been developed for the benefit of the autism patients.
On the other hand, there are a number of mobile apps assist in monitoring the health conditions of the patients after certain complicated procedures like heart operation. The apps, Instant Heart Rate +, Pulse point, MotionX, Cardiograph and Cardiio [5] are helpful for this purpose. In particular My heart counts app has 30,000 registered users.
In this view point a new Cardiac supporting app ‘TMT Predict’ [6] which is a Treadmill Test (TMT) Prediction app has been proposed for the heart patients to know about their heart condition. The result of the test is positive or negative. TMT is one of the most important diagnosis and monitoring procedures for the heart disease. Working out TMT often makes the patient more panic. To get rid of the worry, the TMT predict app has been proposed as shown in Figure 1. The result of this app determines the necessity for the physician’s consultation. In case of positive result doctor’s assistance is a must otherwise diet control and exercise are advised. This helps the heart patients to reduce the number of TMT tests in their life time.
Mobile apps create an awareness among the people about their health condition. Some apps are paid and some are free. People have the choice of using paid or unpaid apps based on their requirement. However, the accuracy of the apps determines their reputation.
Conclusion
ICT is a boon for the healthcare industry which makes the diagnosis, treatment procedure and monitoring easy and cost effective. Speed of the process has been improved compared to early 20th century. [7] The availability and growth in the mobile apps prove that the emerging technologies are useful for stimulating healthier lifestyles and that their effects are beneficial in terms of important clinical implications.
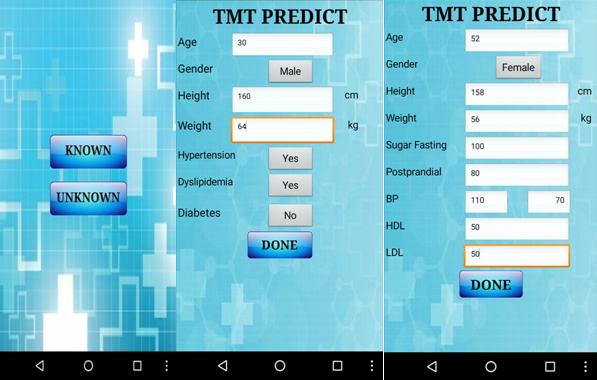
Figure 1. Screen shots of the proposed mobile app “TMT PREDICT”
Acknowledgement
My heartfelt thanks to my research supervisor and mentor Dr. R. Padmajavalli, Head of the Department of BCA, Bakthavatsalam College, Koratur and the domain expert Dr. D.Prabhakar, MD,DM,FACC, Consultant Cardiologist, Ashwin Clinic, Chennai.
References
[1] https://www.practo.com/chennai/clinic/ashwin-clinic-anna-nagar
[2]http://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/tip/Transforming-healthcare-with-video-conferencing.
[3] Zhao, Jing, Becky Freeman, and Mu Li. "Can mobile phone apps influence people’s health behavior change? An evidence review." Journal of medical Internet research 18, no. 11 (2016).
[4] http://www.healthline.com/health/diabetes/top-iphone-android-apps#5
[5] http://www.healthline.com/health/heart-disease/top-iphone-android-apps
[6] A. Jerline Amutha, et al., A Novel Approach for the Prediction of Treadmill Test in Cardiology using Data Mining Algorithms implemented as a Mobile Application, Indian Heart J (2018), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ihj.2018.01.011
[7] Recio-Rodríguez, José I., Carlos Martín-Cantera, Natividad González-Viejo, Amparo Gómez-Arranz, Maria S. Arietaleanizbeascoa, Yolanda Schmolling-Guinovart, Jose A. Maderuelo-Fernandez et al. "Effectiveness of a smartphone application for improving healthy lifestyles, a randomized clinical trial (EVIDENT II): study protocol." BMC Public Health 14, no. 1 (2014): 254.