Information technology plays a crucial role in almost all industries determining their growth and expansion. The healthcare BPO industry is no stranger to this phenomenon and the evolution of IT will continue to increase the demand for more specialised services.
A recent Accenture report says that nearly 66 per cent of health systems in the US will have self-scheduling by the start of 2020. That there will arise the need to focus on training machines just as much as training employees in the next 3 years, will be yet another impact of technology in the healthcare industry predict experts. What does this mean exactly? Probably this could mean more intelligent software, newer algorithms and advanced machine learning.
Studies from Markets & Markets indicate that the US Healthcare BPO Market is estimated to be worth $141.7 Billion by 2018. Approximately 75 per cent of the US companies are said to outsource their work to external locations. Medical coding, medical billing, transcription services, insurance claims and adjudication, Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) and clinical outsourcing, are some of the services that are commonly outsourced among others. This BPO outsourcing market is propelled to grow owing to various government regulations and reforms, measures to reduce healthcare cost, and the increased use of Electronic Health Records (EHRs). Developments and innovation in information technology and regulatory changes are the other key factors furthering the growth and advancement of this industry.
The use of Information Technology in the healthcare industry started as early as the 1960s. The abilities and advantages of computers were slowly being recognised in the healthcare domain. This was an era where hospitals and healthcare providers shared expensive mainframes and storage owing to the expansive and large sized computers and peripheral storage devices. The 70s saw the development of the Problem Oriented Medical Information System (PROMIS). Applications were implemented to automate manual and routine tasks. Hospitals and healthcare units began integrating applications so that financial and clinicalsystems could work in union, minimising administrative paperwork. Moving from discrete departmental systems that were transactional in nature in the 70s to integrated applications and networking solutions in the 80s, the presence and use of IT across the healthcare industry has proliferated.
At the early beginning of the 1990s the healthcare industry was being driven by competition and consolidation was rampant. This was a period that saw the boom of ICT and internet in general, with computers and technology being available in each and every household and industry. The need to implement and harness the benefits of ICT was evident in the healthcare service industry.
There was a radical albeit gradual, shift from process-oriented systems towards patient centred, outcome-oriented systems that became the focal point of healthcare automation. The use of PDA’s to capture data at the point-of-care saw daylight during this period. Integrated delivery network (IDN)-like integration, including the impetus to integrate data and reporting, started emerging.
All these led to the need for more integrated hospital, provider, and managed care offerings in the healthcare BPO industry towards the end of the 90s.
The early 2000 saw increasing demand for enhanced decision support using IT. Integration and the start of outcomes-based reimbursement were the factors driving the US healthcare industry. Technology was being implemented to increase mobility and move gradually towards Electronic Medical Records EMRs. EMRs and EHRs were being widely adopted with the HIPPA act being passed by the Congress in the late 90s. This was also to create a more global digital healthcare infrastructure and enable a seamless flow of information within this infrastructure. Emerging cloud computers and cloud-based big data analytics were other factors that were driving customer requirements for more value added services over and above the regular automation and data entry services.
The period also saw the development of Health Information Exchanges (HIEs), formerly called RHIOs (Regional Health Information Organization), along with the establishment of Health Information Technology Standards Panel (HITSP) and National Alliance for Health Information Technology (Alliance).
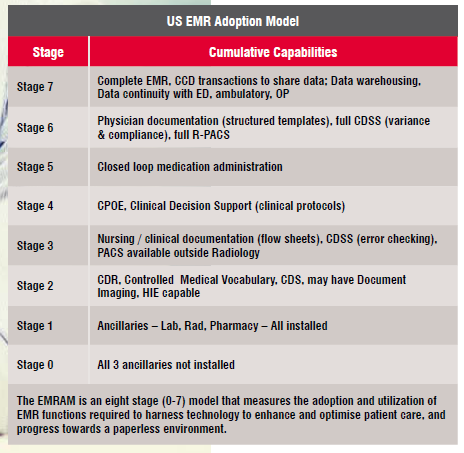 7 Stages of Technology Advancement in Healthcare
7 Stages of Technology Advancement in HealthcareOver the years Healthcare Information Technology (HIT) strategies have evolved to a point where Healthcare Information Systems (HIS) have emerged to be a critical requirement for the healthcare industry. Global healthcare advisor Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) Analytics have launched two models: Electronic Medical Record Adoption Model (EMRAM) and Outpatient Electronic Medical Record Adoption Model (O-EMRAM) to monitor and measure EMR adoption. The EMRAM is an eight-stage (0-7) models that score hospitals and clinics around the world relative to their EMR capabilities. The O-EMRAM eight-stage model measures the adoption and utilisation of EMR functions and O-EMRAM. This model is intended for clinics where there is an encounter between a caregiver and a patient, and the caregiver is licensed to assess, diagnose, treat, prescribe and generate orders and documentation.
The Q4 2016Acute EMRAM adoption analysis released by HIMMS indicates that approximately 60 per cent of the providers are in between the Stages 5 & 6. These are advanced stages in the technology adoption model indicating that at every instance of patient interaction with the healthcare providers, all orders are entered electronically, which enables clinical decision support interaction, and all reports are electronically submitted, thus leading to the creation of a consolidated digital personal health record. In the process, huge amount of data is being generated daily. Data is available in medical coding and billing, processing and adjudication, and across the entire cycle of revenue cycle management.
With more and more healthcare providers adopting the EMRAM Models and advancing to Stages 6 &7, the demand for more value-added service from the healthcare service and solution providers will only increase. There is a growing need to improve operational performance to provide enhanced, cost effective healthcare services, leading to the necessity of integration of healthcare systems and analysing the readily available digitised data.
Regulatory reforms such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) re-emphasize the need for  healthcare services that are more customer/patient-centric and economical. With the advent of technology, consumers demand services that are more flexible—preferring choices on the mode of delivery of services, multiple payment options and much more—to suit their convenience. This augments the responsibility of providers to give the end consumers value-added services, while keeping a check on the cost and not slipping on the quality.
healthcare services that are more customer/patient-centric and economical. With the advent of technology, consumers demand services that are more flexible—preferring choices on the mode of delivery of services, multiple payment options and much more—to suit their convenience. This augments the responsibility of providers to give the end consumers value-added services, while keeping a check on the cost and not slipping on the quality.
For this to happen the focus would have to be on merging the clinical systems, financial systems, and patient satisfaction systems and work on the analytics derived thereof. All these propel the need for data warehouse management and complex analytics solutions that will enable more strategic decisions for healthcare service providers, as well as dashboard reporting providing snapshot of information about the hospital management.
Analytics in the healthcare industry is now going beyond just data management. Better data leads to better insights and thereby improved outcomes. Predictive Analytics and Big Data are the way forward in the healthcare industry. They are seen as key tools to help predict epidemics, cure diseases, improve quality of life, economies of scale quality of healthcare. Analytics can help improve the overall patient-outcome.
Providers feel that with the help of analytics, they will be able to understand as much as they can about a patient and his healthcare history, as early as possible, pick up warning signs of any alignments or chronic disease, administer preventive and better care as well as reduce readmission rates. At the management level, many healthcare organisations that have already implemented analytics, see improved decision making, hospital operational performance and improved financial reporting capabilities as direct benefits.
Big Data, when used across the entire span of revenue cycle management, can help the healthcare organisations reap more benefits. Starting with billing and collection cycle, to tracking payment and denial management, Big Data can help improve revenues.
Insurance claims are denied for a myriad of reasons impacting the Accounts Receivable (AR) cycle and eventually the profits for the providers. With the help of Big Data, the history of denials can be analysed to identify the top reasons and prepare insights which can be worked upon. Based on these insights, pre-checks can be built into the RCM system to process only those claims that have the request information and auto-approve them.
Big Data can also help in reducing the collection period. The time and effort spent in recovering claims can be analysed and the optimal time determined. This will help set a threshold limit on the revenue collection time and identify and follow-up on those that exceed the set limit. This will help strategise the Accounts Receivable (AR) collection period on a real -time basis and improve profitability.
With the Internet of Things (IoT), the impact of wearable technology in the healthcare industry, and the use of the data generated from such devices cannot be ignored. A study from Aruba predicts that nearly 89 per cent healthcare organisations will adopt IoTby 2019. Organisations are slowly adopting the many benefits of wearable technology such as monitoring vital stats, reminding patients to take medication, possibly monitor their health conditions and, in some cases, modifying medication too.
With such complex systems of digitised data available, analytics and innovations are the way forward for the healthcare industry. Electronic Data Warehousing (EDW) and analytics with the ability to mine into the pet a bytes of patient information, understanding the meaning of historical and real time data to predict future outcomes, are now being widely adopted. Organisations need to adopt a data warehouse model that can easily adopt the advances in big data and other analytics.
Information technology will continue to play a major role in the evolution of healthcare services. Be it the payer services, provider services or pharmaceutical services, technology and harnessing the digital data that are stored in silos across departments, will drive solutions that the BPO organisations deliver to their customers.