Employee Engagement of Generation Y Employees
Analysing the impact of talent management and responsible leadershipA post-pandemic revival
The aim of this study is to evaluate the impact of responsible leadership and talent management on employee engagement on gen Y employees working in the healthcare sector of the United Kingdom (UK). This study collects data using a simple random sampling technique, and 52 frontline employees are selected from 11 NHS hospitals in the United Kingdom. This study uses quantitative research methodology and collects data through a questionnaire that has been formulated using a 5-point Likert scale. Data analysis is carried out using SPSS statistical technique, and Pearson correlation and regression analysis are used to analyse the relationship between independent variables, i.e., talent management and responsible leadership, with the dependent variable, i.e., employee engagement. The findings of this study show that talent management and responsible leadership have a positive and significant relationship with employee engagement in the healthcare sector in the UK. This study contributes to the National Health Services (NHS) and explains under what conditions and how employees can be engaged. Consequently, it has both theoretical and practical implications. Lastly, the study lasted about two months and the names of the NHS hospitals and employees have been kept anonymous.

Human capital has a crucial role in any hospital system. It is widely accepted that hospital systems with the best people (doctors, nurses, etc) survive in the market for the long term (Pandita & Ray, 2018). In parallel to this argument, the most important concerns of any hospital leader are their human capital and people resources (people, people, people). Increasing connectivity and globalisation have enabled all organisations to stay more connected, indicating the need for robust policies for human resources management. According to Jauhari, Sehgal & Sehgal (2013), human resources (people, work environment, work conditions, and pay) have a crucial role in attaining organisational goals; organisation s must strive to support all employees to keep the quality and sustain positive attitudes and behaviour that help a company become competitive as compared to its rivalries in the marketplace. One of the most important concepts to ensuring competitiveness and relevance is employee engagement. Employee engagement is regarded as important for improving the quality of organisational human resources (Sadeli, 2015). Employee engagement is the formation of job satisfaction, employee commitment with the firm and their behaviour towards the organisation.
It is further defined as a condition where employees see themselves joyous with work, feel wanted and appreciated by management and as a result become key drivers of vision, mission and purpose of the organisation (Nwabueze, 2023). Hence, scholars define employee engagement as a positive state of mind that is attributed to vigor, commitment, and absorption. Scholars provide other viewpoints and define variables that affect employee engagement like job attributes, the viewpoint of employees towards organisational support, leaders' support, acknowledgement and support, identification with their firm and job, justice and equality provided to them in organisational procedures. All these variables have a positive relationship with employee engagement.
Scholars also describe leadership as one of the most important aspects in an organisation that has a considerable impact on employee engagement and their organisational identification (Aljunaibi, 2014). In contemporary organisation s, the emerging concept, responsible leadership is a subject of discussion due to the increasing inclination of the organisation towards ethical and moral values. Leadership is defined as the process of influencing subordinates and giving them directions to attain their optimal performance (Mousa & Ayoubi, 2019). Leadership has an important role in affecting employee engagement, and a range of scholars have developed a positive linkage between leadership and employee engagement (Hughes & Rog, 2008). As per Goestjahjanti et al. (2020), such leaders are aware of their moral values, viewpoints and understand the value of making sustainable business decisions that consider the interest of all stakeholders. O’Connor & Crowley-Henry (2019) argued that responsible leadership follows a pattern of behaviour that is inclined towards exhibiting positive ability and a positive organisational environment. Eventually, it leads to positive self-growth and enhances confidence amongst employees. O’Connor & Crowley-Henry (2019) found that responsible leadership creates an environment of trust that keeps employees bound to each other. This specific leadership is widely acknowledged to enhance employee engagement and strengthen employee identification with the firm by establishing positive feelings. Each firm has its leader through whom employees feel an attachment with their work and organisation . A stream of the literature shows a positive relationship between responsible leadership and employee engagement (Silzer & Dowell, 2009). Findings from Mousa & Ayoubi (2019) show that responsible leadership has a direct and positive relationship with employee engagement, which is further affirmed by Nugroho (2017) in the context of the service sector, indicating a strong and positive relationship between leadership and employee engagement.
Along with the identified variables, responsible leadership and employee engagement, talent management has an equally important role in the firm. As per Aljunaibi (2014), talent management is the firm's process to enhance its human resource management and meet its requirements. Scholars provide another understanding (e.g., Dhanalakshmi & Gurunathan, 2014) about talent management that it is a comprehensive process that aims to create the highest potential amongst people in the firm through training and development, career growth opportunities and job enrichment that are in parallel to the firm goals and objectives. Various studies have shown that talent management affects employees’ commitment and engagement with the firm. Research carried out by Silzer & Dowell (2009) and Sadeli (2015) found that employee engagement has a positive relationship with talent management.
Talent management with its focus on employee engagement is the fastest-growing concept across firms, businesses are competing because of their talented employees and improving their operational culture. According to Taneja, Sewell & Odom (2015), talented people can perform well and have a high potential to help the firm attain its long-term objectives. Hence, talent management seems a major contributing factor in the competitive workplace and attains sustainable organisational productivity. Hence, scholars recommend that organisation s should continue fostering their strategies towards talent management with a fundamental focus on engaging the workforce daily through flexible work schedules (Doh, Stumpf & Tymon, 2011). Specifically, to generation Y that are regarded as boomers and the digital generation (born in the 1980s and early 2000) have a considerable inclination towards engagement, and scholars find enthusiasm amongst gen Y employees towards talent management and talent acquisition through development. Generation Y employees are energetic and technology savvy and have their working styles different from previous generations (baby boomers). Such employees put considerable focus on learning and career growth opportunities while focusing on organisational values and strategic objectives. If employees from gen Y do not find such growth opportunities and inadequate organisational orientation towards ethics and morality, they switch their job and seek new career prospects (Miska & Mendenhall, 2018). Hence, retention and engagement of such young employees are important as they are attributed to several elements like skills, knowledge, and their ability to learn in the firm (Gond et al., 2011).
Many scholars have identified the importance of talent management, responsible leadership, and employee engagement, yet recent studies identify the need to examine the role of talent management and employee engagement in the hospital sector (Fragouli & Alhaider,2020; Mwawasi, 2021). Hence, this study tends to bridge this empirical and theoretical gap in the literature and examine the influence of talent management and responsible leadership on employee engagement in the Gen Y employees.
Objectives
This study has two important objectives:
- To empirically examine the linkage of talent management activities (training and development of employees, job enrichment prospects and motivation) with employee engagement (commitment, vigor and absorption) amongst Gen Y employees.
- To explore the relationship between responsible leadership (awareness towards employee requirements, moral and ethical values towards subordinates, vision, and responsibility) and employee engagement (commitment, vigor, and absorption) amongst Gen Y employees (Frangieh & Yaacoub, 2017).
Contribution towards Academic literature
This study has an important impact on the academic literature and implications for managers in the hospital sector. First, it explains the influence of talent management and responsible leadership on employee engagement and contributes to the theoretical literature to help future researchers extend their studies. Second, it bridges the empirical gap and carries out primary research to identify the relationship between talent management, responsible leadership, and employee engagement through quantitative research methodology. Third, it tends to help the NHS have grounded theory research information about why and in which instances employees can perform better. Finally, through this paper, HR practitioners can make informed decisions and create a compelling and fun workplace.
Literature review
Talent management
Scholars put forward the description of talent management as to the set of organisational strategies for preparing and managing employees (Pandita & Ray, 2018). As per Goestjahjanti et al. (2020), talent management approaches are well-planned strategies to manage human resources so that organisation can maintain and retain its talented employees and the organisation remains productive. Talent management is a process that starts from recruiting talented people and then developing these people to retain them in the firm. In contemporary organisation s, since employees have a considerable emphasis on career growth opportunities, a talent management program is developed to facilitate its talented employees and enhance their work engagement. This study explains talent management in the following three dimensions: training and development, job enrichment, and motivation through career development opportunities. These dimensions are explained by scholars as the process of establishing talent management and offering employees clear training and development plans and enriching their job that helps them grow their skills (Lin, Huang & Huang, 2020).

Responsible leadership
According to O'Bryan & Casey (2017), responsible leadership is the process of making responsible decisions that consider all stakeholders and their emotions, preferences. Hongal & Kinange (2020) also defined responsible leadership as a positive mental process in the service sector, and it provides self-awareness and a positive attitude that is governed by leaders and promote self-growth amongst employees. Responsible leaders are explained as the state of mind and positive attitude of a leader who promotes growth both in himself and in his subordinates. On the other hand, O’Connor & Crowley-Henry (2019) defined responsible leadership as the pattern of behaviour that encourages self-awareness and moral viewpoints and ethical behaviour through relational transparency. These arguments show that responsible leadership is interpreted as the positive mental state and attitude that is shown by a leader who thinks that his values and beliefs have an important role on employees. This study has used the following dimensions of responsible leadership, previously proposed by Dzimbiri & Molefakgotla (2021). The authors said that such leaders have self-awareness towards their peers and subordinates. Second, these leaders have ethical and moral values for their employees’ and exhibit responsibility for their employees. Leaders who have this behaviour will always seek others' opinions and have values for its peers, colleagues, etc. These dimensions are used to measure responsible leadership amongst 11 NHS hospitals in the UK.
Employee engagement
Employee engagement is about creating an engaging, enabling, and fun work environment that values, appreciates and rewards employee efforts directed at accomplishing organisational goals (Nwabueze, 2023). For Lin, Huang & Huang (2020), employee engagement is defined as a positive, fulfilling job that is linked with the state of mind and is attributed by passion, dedication, and commitment. This explanation can better explain that employee engagement illustrates employee’s connection and indulgence with an organisation through dedication and commitment. Two dimensions of employee engagement are explained by Sheehan, Grant & Garavan (2018): acknowledging the mental, physical, and cognitive energy exerted by employees and providing competitive rewards that meet the individual objectives of the employee (Sheehan et al, 2018).
Furthermore, Antony (2018), contends that employee engagement includes three important indicators; vigor that explains a person's enthusiasm and attitude at the workplace and is attributed to a person's high level of strength and the desire to thrive at the workplace and earn even with persistent difficulties. The second variable is the commitment that is attributed to a person's feelings and is full of inspiration, pride and accepts risks in their workplace. Those who score high in this commitment are more identified with their workplace as it makes them valuable and challenging (Savanevičienė & Vilčiauskaitė, 2017). Other than that, they feel excited and proud at their workplace.
On the other hand, those who score low on commitment does not mean that they do not commit themselves with their work, but they do not have any meaningful and challenging experiences, and they are unenthusiastic about their work. The third is the absorption that is to stay preoccupied at the workplace. Employees are full of persistence, and they have a serious attitude towards their job. In their work times, they feel fast and find it very difficult to detach from their work. This study has used the following three variables, i.e., commitment, absorption, and vigor, as dimensions to explain employee engagement.
The influence of talent management on employee engagement
The process of talent management begins when an organisation starts its recruitment, growth and development of employees who are outstanding performance. The talent management process has a good impact on the employee engagement and results in better performance of the firm through reduced employee turnover and retains high talent (Ahsan, 2018). When the workload is provided by a firm to its employees, and it is low, employee engagement is also low. Scholars further explain this as the career development opportunities provided by the organisation to its employees. This study has also used talent management as the employee job enrichment process and their training and firm support for their employees through motivation to attain employee engagement. Talent management activities and firm HR policies have a considerable impact on employee engagement. Talent management activities, i.e., recognition, career development opportunities and training and development, are used in this study and positively impact employee engagement. This study has focused on the significance of employees' workplace engagement and their engagement with the organisation. Thus, the following hypothesis is formulated.
H1: There is a significant and positive relationship between talent management and employee engagement.
The impact of talent management on responsible leadership
Previous studies show that there is a positive and direct relationship between responsible leadership and employee engagement. The findings by El Masri, & Suliman (2019), showed that the relationship between responsible leadership and employee engagement is facilitated by their organisational talent management. Another study by Lin, Huang & Huang (2020) found that responsible leadership and employee engagement have insignificant relationship since awareness towards employee needs does not exhibit any relationship with employee engagement; however, other studies confirm that employees' needs have a considerable role when leaders want to exercise their responsibility and showcase their generosity towards employees. Many studies have shown that employees do not meet their leaders daily, which shows that the relationship between employees and their leaders is still not significant and needs to be proven by their role of calling as an influencer in the firm (Pandita & Ray, 2018). Hence, the second hypothesis of this study is formulated as.
H2: There is a significant and positive relationship between responsible leadership and employee engagement.
Methodology
Sample and data collection
This study uses an empirical investigation with the employees working in 11 NHS hospitals. Frontline employees are the subject of the study. The population includes 11 hospitals. Data was gathered from the frontline employees. The data was gathered through questionnaires which were distributed to the employees. Such employees’ growth and development can directly affect patients and hospital productivity.
This study uses a deductive research approach, and theory is tested to accept/reject the hypothesis. A cross-sectional time frame is used to collect the data, as this study gathers data only once from the respondents. A total of 52 sample respondents were selected using a random sampling method influenced by an earlier study conducted by O’Connor & Crowley-Henry (2019). One or two frontline desk employees were selected to take part in the study; therefore, an equal opportunity was provided to each hospital selected for this study. The response rate was 95 per cent for female participants and 5 per cent for male participants, which shows that females primarily dominate the NHS.
Moreover, a total of 45 per cent of respondents were from the age group 24 to 30 years and 35 per cent were from 31 to 36 years, and 10 per cent were from 37 to 42 years, and 10 per cent were from 43 to 47 years.
Measures
This study uses a scale that is chosen from previous studies and has used them in this study to evaluate the items of the study. The respondents of the study assessed items using a 5-point Likert scale that states 1 for strongly agree and 5 for strongly disagree. Previous studies are used to select variables of the study and to construct questionnaires in this study. This study uses sub-variables for each selected variable of the study; i) talent management, i.e., training and development of employees, job enrichment prospects and motivation (Hafez et al., 2017) ii) employee engagement, i.e., commitment, vigor, and absorption (Schaufeli et al., 2002).; iii) responsible leadership, i.e., awareness towards employee requirements, moral and ethical values towards subordinates, vision, and responsibility (Walumbwa et al., 2008). All these variables are assessed for the current study by making use of scales from the aforementioned studies. For employee engagement, Utrecht workplace employee engagement is used. Finally, analysis is carried out using statistical package software SPSS that helps to analyze correlation and regression tests of the study.
Results
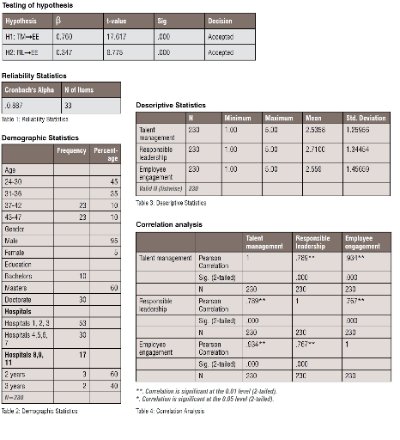
This study uses Pearson Correlation analysis to assess the correlation between independent variables i.e., Talent management and responsible leadership and dependent variable i.e., employee engagement. Table 1 shows the reliability test and table 2 demographic analyses, table 3 descriptive statistics and Table 4 shows Pearson correlation analysis that has been carried out in this study to evaluate the relationship between independent and dependent variables (See appendix).
This study also has shown positive statistical values of the variables and shows that there is a direct and positive association between independent and dependent variables. Furthermore, this study uses reliability analysis through Cronbach alpha that is calculated 0.887, which is greater than the rule of thumb (0.7) and a standard value used to evaluate the scale items’ reliability. The value exhibits that the scale items used in this study are all reliable and show authentic results (see appendix).
The association between talent management, responsible leadership and employee engagement is shown using correlation analysis. The coefficient is evaluated to determine the value of beta that is used to illustrate how well the data supports the hypothesis of the study. Furthermore, this study uses beta coefficients to show the degree of changes identified in the dependent variables of the study for their relevant independent variable. The results clearly show that the path coefficients for each variable are statistically significant at p < 0.05.
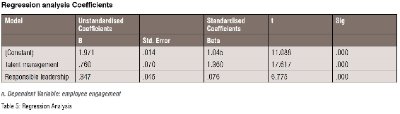
Moreover, the findings show these results for the hypothesis of the study using regression analysis and identify that the dependent variable (employee engagement) is 89 per cent explained by independent variables, i.e., talent management and responsible leadership. The results for hypothesis 1 show the following results: talent management and employee engagement =0.760, t = 17.617, p < 0.05 that exhibits a positive relationship between the variables of the study and support hypothesis 1 of this study. Hypothesis 2 is also tested for to examine the variables of the study, responsible leadership and employee engagement and shows following results; =0.347, t = 6.775, p < 0.05, and shows a positive relationship between the variables of the study. This also supports the second hypothesis of the study; hence, null hypothesis is refused.
Discussion and Findings
Discussion
5.1.1 The impact of talent management on employee engagement
Given the research hypothesis, this study concludes that talent management has a significant and positive relationship with employee engagement in the NHS. The first hypothesis of the study is accepted as the value of t is greater than 1.96 and p-value is less than 0.05, which shows a significant and positive impact of talent management on employee engagement. This shows employee engagement in any organisation is increased if there is an increased focus on talent management. These findings are in line with the studies by El Masri, & Suliman (2019) and Pandita & Ray (2018) and shows that there is a positive relationship between talent management and employee engagement. A study by Taneja, Sewell & Odom (2015), concluded that career planning and development approaches used with rewards and additional incentives could improve employer's commitment to the firm and their ability to absorb is also increased. This shows that employee engagement and commitment with the firm is enhanced. Therefore, organisation s offer various career development programs as their strategy to enhance employee commitment with the firm. This is also supported by Pandita & Ray (2018) that talent management has a significant and positive impact on employee engagement. They further argued that the following dimensions: training and development of employees and job enrichment prospects have a positive and direct impact on employee commitment and vigor. When employees feel attached to the organisation , they are more psychologically linked to their assigned roles and duties, thus increasing overall productivity.
Silzer & Dowell (2009) also supported that talent management activities influence employee engagement where the aspects of organisation al support, and motivation influence employee engagement and improve their commitment to the firm. On the other hand, a quantitative study conducted by Miska & Mendenhall (2018) showed that talent management activities, i.e., training and development, job enrichment and recognition of employees, have positive linkage with employee engagement. Hence, this study carried out in the National Health Service (NHS) confirms previous studies and concludes that if employees are provided with adequate training, developmental opportunities, job enrichment, increased pay/rewards, personal/team recognition, their commitment and dedication to patient care is strengthened. Based on these findings, the mean viewpoint of employees towards motivational strategic approach has a strong relationship with employee engagement, and the viewpoint of evaluating talent management attains high criteria. One of the key aspects that has the highest value is t job enrichment approaches; thus, employees feel encouraged and motivated to act well and retention is equally increased. Although a detailed analysis of this study shows that employees’ viewpoint on the items suggesting that hospital management must institute better retention strategies based on use of newer technologies like AI and flexible work schedules.

This study suggests that the British National Health service must incorporate motivational strategies regardless of whether it is the conservative or labour party that is power. A political free work environment is what the NHS needs to offer better career growth opportunities.
5.1.2 The impact of responsible leadership on employee engagement
Given the findings of this study, and confirmation of the second hypothesis, this study affirms that responsible leadership has an important impact on employee engagement. Thus, the second hypothesis of this study is also accepted, and the null hypothesis is rejected. This shows that responsible leadership has a direct and strong association with employee engagement. A study by Frangieh & Yaacoub (2017) found that responsible leadership is directly related to employees' improved commitment to the firm. Miska & Mendenhall (2018) concluded that responsible leadership with responsibility and vision towards employees have a positive relationship with employee engagement and improve their job satisfaction, suggesting better employee performance. This study is of the view that responsible leadership has a considerable impact on employee engagement through managerial awareness of employee needs, moral and ethical values, and clearly defined organisational direction devoid of politics, but centered around patients and them, the worker bees.
Managerial implications
The current study has several practical inferences and offers managers of the hospital systems to follow a comprehensive framework that could help them improve their HR strategies to cater to frontline employees. Hire and select leaders/managers who have a philosophical focus on employee-first mentality, ethical and moral values and a strategic and operational focus on patient care and caring.
Conclusion
This study concludes that talent management and responsible leadership have a direct, significant, and positive relationship with employee engagement in Gen Y employees working in the NHS. Since employee engagement affect employees’ decision to remain in the organisation or to leave their firm; thus, through robust strategies, hospitals should attempt to enhance their relationship between their leaders and employees and create a sense of loyalty. Furthermore, it is also concluded that the HR managers can also improve their employee retention programs. Employee retention is a key challenge in contemporary organisation s when employee engagement strategy requires how a worker views their whole work experience and the treatment they get from their direct manager. People do not quit their jobs they quit their managers.
Limitations and suggestions for future research
This study has certain limitations that can be used by future scholars to expand the subject of the study. First, this study uses empirical investigation and has collected data using a cross-sectional research time frame; however, the longitudinal study can offer better insights and improve the understanding of the variables in this study. Second, this study has focused on the frontline employees, whereas future studies can be conducted on the mid-level employees and low-level managers. This will provide an expanded viewpoint on the wider population as compared to the current study that has focused only on the frontline employees. Finally, this study focused only on gen Y employees.





