Worldwide, people were never so nicely connected as they are today. The indelible mark of the 21st century is the ‘Tech Revolution’. Leaving no field behind, this revolution has changed the world. It has left significant footprints on the shore of human evolution. Many innovations have optimised the productivity of the healthcare delivery system. These technological advancements have made healthcare smarter than ever before. And, the integration of these technologies will be the future of healthcare. Amongst them, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is a potential tool to transform healthcare.
What is IoMT?
IoMT is basically ‘Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare’. In very simple words, IoMT is a connected network of medical devices, software configuration and hardware framework, which allows remote devices to communicate with healthcare providers wirelessly and in a secured way, for the sake of quick and efficient healthcare delivery.
Influencing Healthcare
The impact of IoMT on every aspect of healthcare is not concealed or can’t be repudiated. According to MatketsandMarkets, the market for IoMT is expected to rise to $188.2 billion by 2025 from $72.5 billion in 2020, at a CAGR of 21.0% during this forecasted period[1].
The COVID-19 pandemic has made people realise how important their health is. People have started taking preventive measures seriously. In such cases, IoMT is going to redefine the mode, quality and way of treating patients.
The IoMT ecosystem
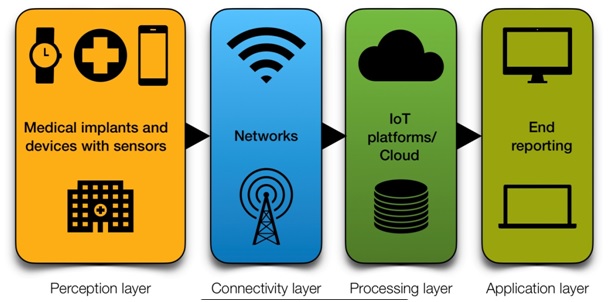
The IoMT mainly works in an extremely well synchronised and coordinated manner through various layers. [Figure 1]
- Perception layer, which manages various smart medical devices across the system. This layer consists of sensors, actuators, machines etc.
- Connectivity layer, which allows data sharing among these devices and cloud through networks and gateways. These gateways act as a connection between LAN (Local area network) and WAN (Wide area network). This layer works through various technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth low energy (BLE), NFC (Near field communication), ZigBee, Cellular networks.
- Processing layer, which is responsible for managing various IoT layers, to streamline the data across the system and to store this data. Once the data is stored, the process of data abstraction starts here.
- Application layer, which aids data analysis, permits reporting to the end users and controls the devices. This data is procured to monitor services, to improve artificial intelligence (AI), to upgrade machine learning, to make business decisions and most importantly, to uplift the quality of healthcare and to monitor patient outcomes.
IoMT can also be classified based on their level of presence:
1. In Vivo IoMT: Smart medical devices which have been implanted inside an individual’s body are In Vivo IoMT. These implants are modifying the way people see healthcare. However, MedTech has succeeded to such a great extent in developing these devices, the concerns like extent of biocompatibility, powering the implant, data handling are still buzzing around.
2. In Vitro IoMT: This can be further sub-classified into,
- On-body IoMT: Wearables devices like smart watches, fitness bands, glucose sensors etc.
- In-home IoMT: Smart medical devices which can share the data regarding oxygen saturation, blood pressure and other measures with healthcare providers. Personal emergency response system (PERS) tracks events such as a fall or a heart attack and immediately informs healthcare providers.
- In-community IoMT: It is extremely useful to respond to emergency situations. Ambulances or vehicles transporting patients or vital medical resources can be tracked. Healthcare needs of remote areas can be satisfied adequately.
- In-hospital IoMT: To improve quality and standards of healthcare services, various sensors, smart devices, ultra fast connectivity, integrated data processing systems are used. Hospital administrators should have a comprehensive perception of what is happening around them and what the patient’s outcome is after putting so much effort into it.
Benefits of IoMT
- Improved healthcare services: IoMT allows an integrated and holistic approach to deliver healthcare services. This will reduce the cost of expensive services. Consistency of care and continuity of treatment will improve the patient compliance. IoMT can deliver a focused outcome which will increase the efficiency of healthcare providers. Assimilating technology with medical science will make the healthcare system more patient centric and, in order to that, value-based care will gradually replace the conventional healthcare model.
- Remote patient monitoring: Physicians can monitor patients remotely with the help of IoMT. A doctor can virtually take a round of ICUs or wards. He or she might be chilling on the beach of Goa and can still manage to look after their patients. They can go through patient’s reports, digital imaging, electro physiological studies on their smartphones. Health services can be delivered to remote places rapidly. Old aged or disabled patients can be counselled and treated remotely. Healthcare providers can promptly respond to emergencies like sudden cardiac arrest or myocardial infarction or sudden trauma. Johnson & Johnson, in collaboration with Apple, is working on the Heartline™ Study, which is an app-based, randomised, controlled, virtual research study. It aims to assess if a heart health engagement program provided through the Heartline™ Study app on iPhone, in combination with the ECG app and the irregular rhythm notification feature on Apple Watch, can reduce the likelihood of stroke and improve health outcomes with the earlier detection of Atrial Fibrillation[2].
- Personalised healthcare services: Prescribing drugs, delivering care, treatment of choice and a lot of many other things vary according to age, sex, phenotype, pre-existing conditions, family history, demographic factors and so on. Machine learning and data analysis allow service providers to deliver a more personalised delivery of care.
- Increased doctor-patient engagement: IoMT will allow physicians as well as patients to stay in touch for longer periods, which in turn will increase the engagement between them. This mutual engagement and trust will be translated into better patient outcomes.
- Empowered decision making: Analysing these myriad pieces of data across the system, global healthcare management leaders will be motivated to make better and focused decisions. This will open up a completely new space to adapt advanced business models.
- Hospital asset management: Medical and paramedical staff will get more time to concentrate and focus on treating patients rather than spending their time and energy on streamlining and managing various hospital assets. IoMT will also help with monitoring medical equipment. An upgraded and evolved Hospital information management system (HIMS) can be developed which can store and manage patient’s data, hospital data, medical resources data and many other things. The Electronic healthcare records system (EHRS) can play a vital role in patient referrals among specialists.
Challenges to combat
Tech leaders like Google LLC, IBM, Apple Inc., Microsoft Corporation, Cisco, Oracle, Medtronic plc., GE Healthcare, Johnson & Johnson, Omron corporation, Abbott laboratories, Philips Healthcare, Siemens are actively working to develop IoMT. They have spent a lot of energy and money on R&D also. Technology is moving at a faster speed than the healthcare industry. Hence, MedTech players are facing problems with executing IoMT to its maximum potential.
- Lack of synchronisation: MedTech and healthcare service providers will have to come together to take this challenge as an opportunity to upgrade and evolve. Creating a large impact needs effective, efficient and committed collaboration among all the building blocks of IoMT.
- Cybersecurity: This is the biggest concern related to IoMT. Data privacy is a very sensitive issue. As the patient’s health data gets stored on a third party server, malefactors may breach the security and get access to this data. There are laws to protect data privacy, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) andthe California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). The European Union has also implemented laws like the Regulations for Medical Devices (MDR) and the In Vitro Diagnostic Devices Regulation (IDVR). To solve this problem, Blockchain technology can be used to protect data privacy and a Zero Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA) model should be implemented for IoMT devices. The main concept of this model is “Never trust, always verify”.
- Lack of uniformity and legality: There are multiple devices connected at various layers of IoMT. Not all the devices work in the same manner or in the same framework. In addition to that, at each stage there are various service providers who offer different services. So, it gets difficult to achieve proper integration of different databases because of no uniform protocol for communication, data storage and data privacy. To maintain uniformity and data privacy across the system, software should beHealth Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) and Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH) compliant.
- Interoperability: It is basically concerned with the extent of the data flowing across the system and devices. Interoperability is quite a perplexing problem and depends upon transparent and secured data exchange or communication through strict protocols and consensus standards. The regulatory system should be efficient and effective enough to govern the proper data exchange in systems.
- Overwhelming data: A lot of data gets stored and shared via IoMT. It consumes a lot of energy and powerful servers are needed to store it. Sometimes, excessive information also leads to inaccurate assumptions, which in turn results in difficulty in making a decision.
- High investment cost: Implementing IoMT consumes a huge chunk of money, energy and effort. Tech giants can bear the cost, but not every tech company can tolerate this financial load.
Thus, there are many challenges like these yet to come. But, the future of healthcare looks promising through the window of IoMT. Proactive approaches to bring IoMT and Artificial Intelligence (AI) together, will result in high quality patient care. But as there is no rose without a thorn, no power comes without a dark side, all an individual is expected to use it wisely and for the betterment of humankind. Isn’t it?
Booster dose:
“Learn continually - there’s always ‘one more thing’ to learn!”
-Steve Jobs
References
[1] https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/iot-healthcare-market-160082804.html
[2] https://www.jnj.com/johnson-johnson-launches-heartline-the-first-of-its-kind-virtual-study-designed-to-explore-if-a-new-iphone-app-and-apple-watch-can-help-reduce-the-risk-of-stroke

